Research focus
Turbulence
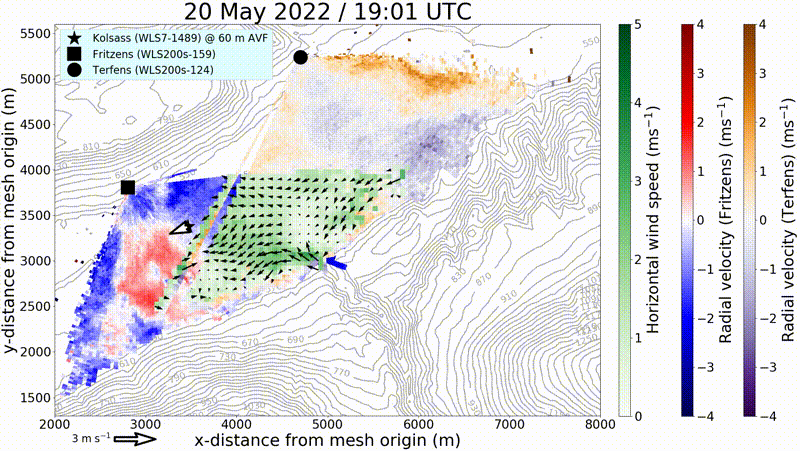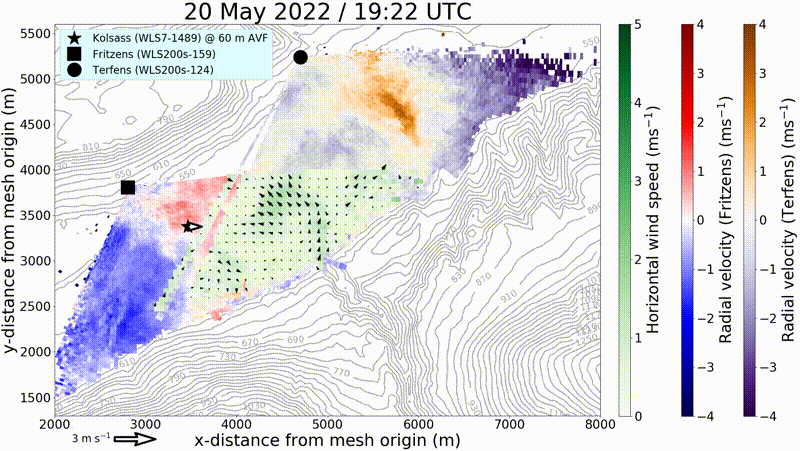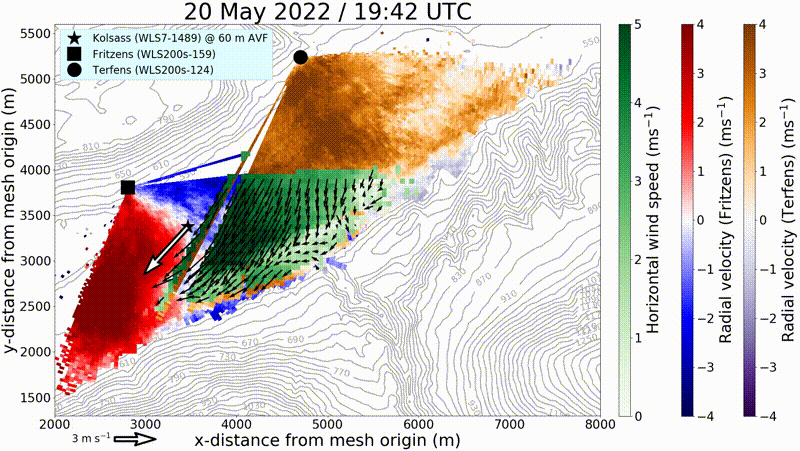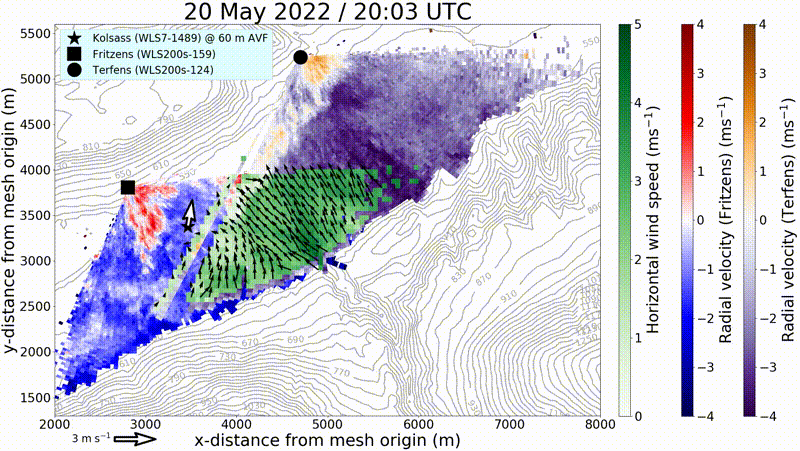
By means of remote sensing and in situ measurement systems, KITcube can probe the entire boundary layer. These measurements enable the identification of both horizontal and vertical structures in the convective boundary layer. Thus, it is possible to survey the structure of gusts and to minimize the statistical error of turbulence measurements.
Convection
Mechanisms for triggering convection over complex terrain and inhomogeneous land use, as well as processes causing deep convection, are still not well understood. KITcube is designed to gain an improved understanding of these processes.
Clouds and precipitation
The formation and development of clouds and precipitation is addressed with KITcube. The instrumentation enables an improved understanding of microphysical processes in clouds and precipitation. Temporal and spatial development of cloud structures and mixing processes can be investigated. Types and properties of hydrometeors are analyzed.
Assimilation and model evaluation
KITcube data capture processes at different scales and allow the evaluation of different types of numerical models, from Large Eddy Simulations (LES) to mesoscale prediction systems. Retrieval algorithms such as applied within Cloudnet can also be validated. KITcube data are ideally suited for assimilation into model systems such as ICON.